Definition
Polycystic ovaries is a very common hormonal disturbance in women of reproductive age. Abnormal or extended menstrual bleedings, an increase in hair production, acne and obesity are often the reasons that will lead a woman to a check. In some cases, difficulty in conception is what leads us to fertility testing and the detection of polycystic ovaries.
Symptoms may vary between people. Some women may experience a delay in their menstrual cycle during periods of anxiety, but there are some who present a severe form of polycystic ovaries syndrome with rare menstruation, obesity, acne and hirsutism.
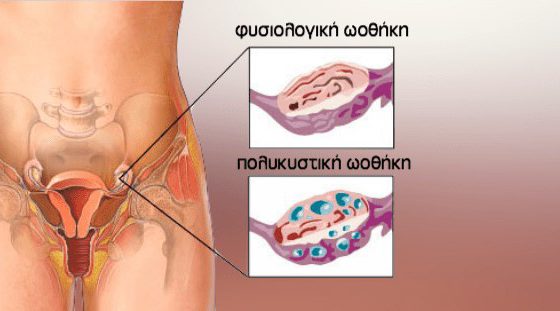
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of polycystic ovaries will be confirmed when two of the following situations arise:
- Abnormal menstrual cycles. This is the most characteristic symptom. In this case, we have longer-lasting cycles of 40 days, or less than 8 cycles per year. Four or more cycles without ovulation. Increased duration of menstruation.
- Polycystic ovaries. In an ultrasound the ovaries appear larger, containing 10–12 small cysts in their periphery.
- Increased androgen production. which results to acne, hirsutism or androgen-induced alopecia.
Causes
The causes of polycystic ovaries are not well understood. However, the following factors appear to play a role:
- Increased insulin production. Insulin is produced in the pancreas and allows ours cells to consume sugars. When a person is insulin-resistant, the pancreas strains to produce more. This insulin excess may cause the ovaries to produce more androgens.
- Low grade inflammation. Studies have shown that women with polycystic ovaries have low grade inflammation. This, in turn, can cause resistance to insulin.
- Heredity. If the mother, the sister and the grandmother have had polycystic ovaries syndrome, it is more likely that the rest of the women in the family will present with the condition.
- Exposure to androgens during intrauterine life. Currently, this is being researched.
Complications
A woman with polycystic ovaries syndrome, which in no case should be confused with an indication of micropolycystic ovaries during an ultrasound, may experience the following complications:
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Disturbance in cholesterol and triglyceride levels
- Increased C-reactive protein (which indicates an increase in the risk of cardiovascular disease).
- Fatty liver
- Gestational diabetes
- Sub fertility (due to anovulatory cycles)
- Endometrial hyperplasia due to the continuous exposure to high levels of oestrogen. This results in an increased risk of endometrial cancer.
Management
A. There is medication that can be helpful in:
1.) Regulating the menstrual cycle
- After a thorough screening, a carefully chosen contraceptive pill may be a good solution. It reduces androgen production and offers the body a beneficial break from the continuous oestogen effects.
- An alternative approach for women who cannot, due to health problems, or do not wish to receive a contraceptive pill, is the administration of progesterone for 10–14 days every 40 days.
- Meformin is an anti-diabetic drug that reduces insulin levels. It regulates the menstrual cycle and ovulation. When a woman follows a healthy diet and exercise programme, it helps with losing weight.
2.) Ovulation
If a woman is trying to get pregnant, it may be required that she is administered treatment with clomiphene citrate which is an inhibitor of oestrogen production. If alone or in combination with metformin, this regimen does not produce any results, we may have to resort to the administration of gonadotrophins.
B. Our lifestyle plays a key role not only in improving the symptoms, but also in the ultrasound appearance of polycystic ovaries.
Maintain a stable weight. Obesity is obviously not helpful. Weight loss reduces resistance to insulin as much as the levels of androgens. Get used to avoiding sugar in its hidden form (take-away, cereal, bread, etc.). Ask your doctor to provide you with a diet programme. It is important that you maintain the habit of eating three meals with 2 small ones in between, in order to maintain blood sugar levels stable.
Learn which the right nutritional habits are. You need to follow a low carb diet. Choose carbohydrates rich in fibre. Increased fibre consumption equals to a slowing in the increase of blood glucose. Such carbohydrates are: whole-wheat bread and cereals, whole-wheat pasta, barley, brown rice, beans. Eat fresh fruits and vegetables.
Be active. Exercise helps in reducing sugar blood levels. Increase your daily activity and exercise. If you are unable to follow a programme at a gym facility, fast walking for half an hour at least every day will help your metabolism regulate your weight.
 English
English Ελληνικα
Ελληνικα



